Friday, March 22, 2013
Aggregation issue with Hyperion Planning
One of my friends recently called and me that the parent in her Hyperion Planning was not aggregating even if the aggregation script was ran multiple times. She double checked the aggregation script and there was no logical or syntax errors. The Parent has multiple children and half of them or dynamic calc and other are store members. What was the issue.
In this type of cases before going aggregation script we must first check the consolidation properties. There was an offshore team in India and they changed the consolidation property to "Ignore" and she was not informed.
Again this issue may look very simple but the order in which we trouble shoot may save time. Instead of banging head looking at aggregation script, we should first check the consolidation property.
What are patches in Hyperion product suite
One of my friends who just started asked me this question. He got confused between
Multi server Hyperion Environment
Patching
Load balancing
I will try to explain in simple terms what the above mean. First lets go to Patching.
Same as humans No software is built perfect, as it was built by humans :-)
When a new version of software is released some of the components of it may not work properly. The issues are generally called bugs. If a particular software has lot of bugs the software development team will combine solutions for all the known bugs into an small additional release called Patch.
For example Hyperion smart view version 11.1.2.2 has some issues to it. Oracle Hyperion combined all the solutions to those issues and released a .300 patch. When you install the patch our 11.1.2.2. version will be now 11.1.2.2.300 version.
similarly for Hyperion planning we have 11.1.2.2.300
How do we know what's included in the patch?
we get all the information about the patch like what bugs it is fixing in the read me document of the patch. The patch can be downloaded from
https://support.oracle.com/epmos/faces/PatchHome?_adf.ctrl-state=1mr4xxdz8_9&_afrLoop=323389713099946
To install the patch is it as simple as double click the .exe?
You need to be careful in applying the patches. You have to read "readme" document first and see if there are any prerequisites. For example Planning may have some prerequisites in foundation etc.,
In a nutshell strictly follow readme document even if you don't like it.
Unable to login to Hyperion Workspace or Planning.
One of my friends got this error which says EPMCSS-0031: Failed to authenticate user. Invalid credentials. Enter valid credentials.
All the services (Hyperion Planning, foundational, APS, EAS) were up and running. The passwords were not changed. She tried to restart the services but no luck.
Finally she checked whether the relational databases which support foundation and planning were up. The prod support told that there was an issue on relational database side and they were down.
The gist of this post is if we have this error, we first need to check whether relational database is running or not, next did anyone change the password and then are the services running are not.
Monday, January 28, 2013
Hyperion Upgrade Issues
I will list all the issues we faced on the road to latest and greatest hyperion product suite.
Issue #1
Its common practice of the users to reuse the smartview templates. When some of my users open smartview templates which were created in older version they get an error "COMMON PROVIDER SESSION TYPE MISMATCH". The error can be resolved by closing the sheet and open it again. However this is very annoying as some of the business users use Smart view for most part of their day. Oracle suggested the following resolution
"
1) Open workbook (Don't refresh),
2) In SmartView panel navigate to the required connection and connect.
3) Right click on connection and click on "Adhoc analysis".
4) Choose the following option on prompt "Reuse sheet content and pov".
5) A message box will display with following info "Old SmartView grid format detected, This operation will convert the grid into the new format, do you want to continue?" click Yes.
6) After that save the workbook and user can continue normally.
"
Wednesday, November 2, 2011
New Hyperion Planning book
good afternoon.
I recently came across book on Hyperion Planning version 11 which is of great quality.
I know author of this book ,Sandeep Reddy , via oracle forums and had good e mail discussions with him in th past. All his posts in oracle forums were very valuable and technical in nature.
I read his recent book and found it very informative and must have if you are working on Hyperion or if you want to plung into Hyperion Planning world.
you can find his book in the following link
http://www.packtpub.com/getting-started-with-oracle-hyperion-planning-11/book
Happy reading :-)
Wednesday, October 19, 2011
Common Essbase Admin Tasks
- Every morning I check status of my Nightly cycle. Nighty cycle is an automation process which builds my hierarchy, clears data, loads data and runs all aggregation and different business logic calc scripts and completes backup.
- Nigthly cycle is my full load. However I also do incremental data load and check the status of the incremental load and check to see if there are any errors or rejects.
- Database Health: Check to see the fragmentation ratio and if it is more than 50 % framented and calc scripts were taking awfull lot of time, then I will initiate dense restructure (which removes fragmentation) that night. Generally dense restructures were not done during week days. Only exceptional cases are entertained.
- As part of nightly cycle my main cube also feeds data to reporting cube. I use dataexport command to export and outline extractor combined with HAL (Hyperion Application Link) to export and format metadata.
- We schedule all the jobs using windows scheduler and automation was done using windows batch files.
- If the calcs are running slow, we check how much database was fragmented, size data cache, outline order etc.
- If Data cache is full, we need to increase the size of data cache. After increasing the size, database needs to be started for it to take effect.
- Stopping and starting database in the nightly cycle is also good practice. It removes cache build up.
- If the database is corrupt or atleast we have a suspicion that database is corrupt we use VALIDATE command in ESSCMD.
- If the database is corrupt we can restore database from backup (discussed in backup post).
- Sometimes essbase service won't start eventhough we start it manually. This is because of any idle process running before essbase went down. Those orphanned (Idle) process won't allow essbase service to start. I use windows process explorer (tool from Microsoft, just like task manager) to kill those idle processes and restart essbase.
Friday, August 12, 2011
Exporting Security out of Hyperion Planning application
SELECT A.OBJECT_ID AS GROUP_ID,
A.OBJECT_NAME AS GROUP_NAME,
D.USER_ID,
E.OBJECT_NAME AS USER_NAME,
D.ROLE,
D.SYNC_PSWD,
FROM
HSP_OBJECT A,
HSP_OBJECT_TYPE B,
HSP_USERSINGROUP C,
HSP_USERS D,
HSP_OBJECT E
Where
A.OBJECT_TYPE=B.OBJECT_TYPE
AND A.OBJECT_ID=C.GROUP_ID
AND C.USER_ID=D.USER_ID
AND D.USER_ID=E.OBJECT_id
AND B.OBJECT_TYPE ='6'
ORDER BY A.OBJECT_ID
Tuesday, March 2, 2010
Hyperion Essbase Knowledge Base
How do you optimize outline?
Usually the outline is optimized using the hourglass design for dimension ordering i.e,
· Dimension with Accounts tag
· Dimension with Time tag
· Largest Dense dimension
· Smallest dense dimension
· Smallest Sparse dimension
· Largest Sparse dimension
What are the ways to improve performance during data loads?
There are several ways to optimize load
1. Grouping of Sparse member combinations
2. Making the data source as small as possible
3. Making source fields as small as possible
4. Positioning the data in the same order as the outline
5. Loading from Essbase Server
6. Managing parallel data load processing
What are the design considerations for calculation optimization?
You can configure a database to optimize calculation performance. The best configuration for the site depends on the nature and size of the database.
· Block Size(8Kb to 100Kb) and Block Density
· Order of Sparse Dimensions
· Incremental Data Loading
· Database Outlines with Two or More Flat Dimensions
· Formulas and Calculation Scripts
When does Fragmentation occur?
Fragmentation is likely to occur with the following:
· Read/write databases that users are constantly updating with data
· Databases that execute calculations around the clock
· Databases that frequently update and recalculate dense members
· Data loads that are poorly designed
· Databases that contain a significant number of Dynamic Calc and Store members
· Databases that use an isolation level of uncommitted access with commit block set to zero
How can you measure fragmentation?
You can measure fragmentation using the average clustering ratio or average fragmentation Quotient.
Using the average fragmentation quotient
Any quotient above the high end of the range indicates that reducing fragmentation may help performance
Small (up to 200 MB) 60% or higher
Medium (up to 2 GB) 40% or higher
Large (greater than 2 GB) 30% or higher
Using the average clustering ratio:
The average clustering ratio database statistic indicates the fragmentation level of the data (.pag) files. The maximum value, 1, indicates no fragmentation.
How do you can prevent and remove fragmentation?
You can prevent and remove fragmentation:
· To prevent fragmentation, optimize data loads by sorting load records based upon sparse dimension members. For a comprehensive discussion of optimizing data load by grouping sparse members.
· To remove fragmentation, perform an export of the database, delete all data in the database with CLEARDATA, and reload the export file.
· To remove fragmentation, force a dense restructure of the database.
Why is database restructuring?
As your business changes, you change the Essbase database outline to capture new product lines, provide information on new scenarios, reflect new time periods, etc. Some changes to a database outline affect the data storage arrangement, forcing Essbase to restructure the database.
What are the types of database restructuring?
The two ways by which a database restructure is triggered:
- Implicit Restructures
- Dense restructure
- Sparse restructure
- Outline-only restructure
- Explicit Restructures
What are the conditions affecting Database restructuring?
Intelligent Calculation, name changes, and formula changes affect database restructuring:
· If you use Intelligent Calculation in the database, all restructured blocks are marked as dirty whenever data blocks are restructured. Marking the blocks as dirty forces the next default Intelligent Calculation to be a full calculation.
· If you change a name or a formula, Essbase does not mark the affected blocks as dirty. Therefore, you must use a method other than full calculation to recalculate the member or the database.
What are the files used during Restructuring?
When Essbase restructures both the data blocks and the index, it uses the files described
essxxxxx.pag Essbase data file
essxxxxx.ind Essbase index file
dbname.esm Essbase kernel file that contains control information used for db recovery
dbname.tct Transaction control table
dbname.ind Free fragment file for data and index free fragments
dbname.otl Outline file in which is defined all metadata for a database and how data is stored
What are the actions that improve performance for restructuring?
There are a number of things you can do to improve performance related to database restructuring:
· If you change a dimension frequently, make it sparse. · Use incremental restructuring to control when Essbase performs a required database restructuring. · Select options when you save a modified outline that reduce the amount of restructuring required.
Which restructure operations are faster?
These types of restructure operations are listed from fastest to slowest:
· Outline only (no index or data files)· Sparse (only index files) · Dense (index files and data files) as a result of adding, deleting, or moving members and other operations · Dense (index and data files) as a result of changing a dense dimension to sparse or changing a sparse dimension to dense
What is Implicit Restructures?
Essbase initiates an implicit restructure of the database files after an outline is changed using Outline Editor or Dimension Build. The type of restructure that is performed depends on the type of changes made to the outline
What is Explicit Restructures?
When you manually initiate a database restructure, you perform an explicit restructure. An explicit restructure forces a full restructure of the database. A full restructure comprises a dense restructure plus removal of empty blocks.
What is Dense restructure?
If a member of a dense dimension is moved, deleted, or added, Essbase restructures the blocks in the data files and creates new data files. When Essbase restructures the data blocks, it regenerates the index automatically so that index entries point to the new data blocks.
Empty blocks are not removed. Essbase marks all restructured blocks as dirty, so after a dense restructure you need to recalculate the database.
What is Sparse restructure?
If a member of a sparse dimension is moved, deleted, or added, Essbase restructures the index and creates new index files.
Restructuring the index is relatively fast; the amount of time required depends on the size of the index.
What is Outline-only restructure?
If a change affects only the database outline, Essbase does not restructure the index or data files.
Member name changes, creation of aliases, and dynamic calculation formula changes are examples of changes that affect only the database outline.
Explain the process of dense restructure?
To perform a dense restructure, Essbase does the following:
1. Creates temporary files that are copies of the .ind, .pag, .otl, .esm, and .tct files. Each temporary file substitutes either N or U for the last character of the file extension, so the temporary file names are .inn, essxxxxx.inn, essxxxxx.pan, dbname.otn, dbname.esn, and dbname.tcu. 2. Reads the blocks from the database files copied in step 1, restructures the blocks in memory, and then stores them in the new temporary files. This step takes the most time. 3. Removes the database files copied in step 1, including .ind, .pag, .otl, .esm, and .tct files. 4. Renames the temporary files to the correct file names: .ind, .pag, .otl, .esm, and .tct.
Explain the process of sparse restructure?
When Essbase does a sparse restructure (restructures just the index), it uses the following files:· essxxxxx.ind· dbname.otl· dbname.esm
What is data compression?
Essbase allows you to choose whether data blocks that are stored on disk are compressed, as well as which compression scheme to use. When data compression is enabled, Essbase compresses data blocks when it writes them out to disk. Essbase fully expands the compressed data blocks, including empty cells, when the blocks are swapped into the data cache.
Generally, data compression optimizes storage use. You can check compression efficiency by checking the compression ratio statistic.
What are types of data compression?
Essbase provides several options for data compression:
1. Bitmap compression, the default. Essbase stores only non-missing values and
uses a bitmapping scheme. A bitmap uses one bit for each cell in the data block, whether the cell value is missing or non-missing. When a data block is not compressed, Essbase uses 8 bytes to store every non-missing cell. In most cases, bitmap compression conserves disk space more efficiently. However, much depends on the configuration of the data.
2. Run-length encoding (RLE). Essbase compresses repetitive, consecutive values --any value that repeats three or more times consecutively, including zeros and #MISSING values. Each data value that is repeated three or more times uses 8 bytes plus a 16 byte repetition factor.
3. zlib compression. Essbase builds a data dictionary based on the actual data being compressed. This method is used in packages like PNG, Zip, and gzip. Generally, the more dense or heterogeneous the data is, the better zlib will compress it in comparison to bitmap or RLE compression.
4. Index Value Pair compression. Essbase applies this compression if the block density is less than 3%.Index Value Pair addresses compression on databases with larger block sizes, where the blocks are highly sparse. zlib does not use this.
5. No compression. Essbase does not compress data blocks when they are written to disk
When do you use RLE over Bitmap Compression?
Use RLE over Bitmap When,
Average block density very low (< 3%).
Database has many consecutive repeating Values.
When do you disable compression?
You may want to disable data compression if blocks have very high density (90% or greater) and have few consecutive, repeating data values. Under these conditions, enabling compression consumes resources unnecessarily. Don't use compression if disc space/memory is not an issue compared to your application. It can become a drain on the processor.
What are data locks?
Essbase issues write (exclusive) locks for blocks that are created, updated, or deleted, and issues read (shared) locks for blocks that should be accessed but not modified. By issuing the appropriate locks, Essbase ensures that data changed by one operation cannot be corrupted by a concurrent update.
What is a transaction?
When a database is in read/write mode, Essbase considers every update request to the server (such as a data load, a calculation, or a statement in a calculation script) as a transaction.
What is transaction control file?
Essbase tracks information about transactions in a transaction control file (dbname.tct).
The transaction control file contains an entry for each transaction and tracks the current state of each transaction (Active, Committed, or Aborted).
What is isolation level and what are the types of isolation levels?
Isolation levels determine how Essbase commits data to disk. Essbase offers two isolation levels for transactions --committed access and uncommitted access (the default).
What is commited access?
When data is committed, it is taken from server memory and written to the database on disk. Essbase automatically commits data to disk. There are no explicit commands that users perform to commit data blocks.
Talk about committed and uncommitted access?
Committed:
Committed at the end of a transaction. Data retained till then.
All blocks in question locked.
Pre-Image Access: If enabled, Read only access allowed
Wait Times:
Indefinite
Immediate Access or no Wait
No. of Seconds Specified
Uncommitted:
Committed only at synchronization points.
Block by Block Locks.
Commit Row: No of rows of data loaded when Sync point occurs.
Commit Block: No. of Blocks Modified when Sync Point occurs.
For Rollback, Commit Row=0 and Commit Block=0
What are the advantages and disadvantages of using committed access?
You can optimize data integrity by using committed access.
Setting the isolation level to committed access may increase memory and time requirements for database restructure.
Which transaction is always in committed mode?
The Spreadsheet Add-in lock and Send and the Grid API are always in Committed Access Mode
What are the memory caches used by Essbase to coordinate memory usage? Essbase uses five memory caches to coordinate memory usage 1. Index Cache 2. Data File Cache 3. Data Cache 4. Calculator Cache 5. Dynamic Calculator Cache
What is Index cache?
The index cache is a buffer in memory that holds index pages. How many index pages are in memory at one time depends upon the amount of memory allocated to the cache.
What is Data file cache?
The data file cache is a buffer in memory that holds compressed data files (.pag files). Essbase allocates memory to the data file cache during data load, calculation, and retrieval operations, as needed. The data file cache is used only when direct I/O is in effect.
What is Data cache?
The data cache is a buffer in memory that holds uncompressed data blocks. Essbase allocates memory to the data cache during data load, calculation, and retrieval operations, as needed.
What is Calculator cache?
The calculator cache is a buffer in memory that Essbase uses to create and track data blocks during calculation operations.
What is Dynamic calculator cache?
The dynamic calculator cache is a buffer in memory that Essbase uses to store all of the blocks needed for a calculation of a Dynamic Calc member in a dense dimension (for example, for a query).
What are the memory caches used by Essbase to coordinate memory usage?
Essbase uses five memory caches to coordinate memory usage
Index Cache: Min -1024 KB (1048576 bytes) Default - Buffered I/O : 1024 KB (1048576 bytes);Direct I/O : 10240 KB (10485760 bytes) Opt -Combined size of all essn.ind files, if possible; as large as possible otherwise.Do not set this cache size higher than the total index size, as no performance improvement results.
Data File Cache: Min - Direct I/O: 10240 KB(10485760 bytes) Default -Direct I/O: 32768 KB(33554432 bytes) Opt -Combined size of all essn.pag files, if possible; otherwise as large as possible.This cache setting not used if Essbase is set to use buffered I/O.
Data Cache:Min - 3072 KB (3145728 bytes) Default - 3072 KB (3145728 bytes) Opt -0.125 * the value of data file cache size.
Calculator Cache:Min - 4 bytes Max: 200,000,000 bytes Default - 200,000 bytes Opt -The best size for the calculator cache depends on the number and density of the sparse dimensions in your outline. The optimum size of the calculator cache depends on the amount of memory the system has available.
What is the structure of currency applications?
In a business application requiring currency conversion, the main database is divided into at least two slices. One slice handles input of the local data, and another slice holds a copy of the input data converted to a common currency.
Essbase holds the exchange rates required for currency conversion in a separate currency database. The currency database outline, which is automatically generated by Essbase from the main database after you assign the necessary tags, typically maps a given conversion ratio onto a section of the main database. After the currency database is generated, it can be edited just like any other Essbase database.
What are the three dimension that should be present in main database of currency application?
The main database outline can contain from 3 to n dimensions. At a minimum, the main database must contain the following dimensions:
· A dimension tagged as time.
· A dimension tagged as accounts.
· A market-related dimension tagged as country.
What are the dimensions that should be present in currency database of currency application?
A currency database always consists of the following three dimensions, with an optional fourth dimension:
· A dimension tagged as time, which is typically the same as the dimension tagged as time in the main database.
· A dimension tagged as country, which contains the names of currencies relevant to the markets (or countries) defined in the main database.
· A dimension tagged as accounts, which enables the application of various rates to members of the dimension tagged as accounts in the main database.
· A currency database, which typically includes an optional currency type dimension, which enables different scenarios for currency conversion.
What are the conversion methods supported by Essbase for currency applications?
Different currency applications have different conversion requirements. Essbase supports two conversion methods:
· Overwriting local values with converted values.
· Keeping local and converted values.
Either of these two methods may require a currency conversion to be applied at report time. Report time conversion enables analysis of various exchange rate scenarios without actually storing data in the database.
What is the process to build a currency conversion application and perform conversions?
To build a currency conversion application and perform conversions, use the following process:
1. Create or open the main database outline. 2. Prepare the main database outline for currency conversion. 3. Generate the currency database outline. 4. Link the main and currency databases. 5. Convert currency values. 6. Track currency conversions. 7. If necessary, troubleshoot currency conversion.
What is CCONV? After you create a currency conversion application, you convert data values from a local currency to a common, converted currency by using the CCONV command in calculation scripts Ex: CCONV USD;CALC ALL;
Can we convert the converted currency back into its local currency? You can convert the data values back to the original, local currencies by using the CCONV TOLOCALRATE command.
When you convert currencies using the CCONV command, are the resulting data blocks are marked as dirty or clean? When you convert currencies using the CCONV command, the resulting data blocks are marked as dirty for the purposes of Intelligent Calculation. Thus, Essbase recalculates all converted blocks when you recalculate the database.
What is CCTRACK? You can use the CCTRACK setting in the essbase.cfg file to control whether Essbase tracks the currency partitions that have been converted and the exchange rates that have been used for the conversions. By default CCTRACK is turned on.
What are the reasons to turn off CCTRACK? For increased efficiency when converting currency data between currency partitions, you may want to turn off CCTRACK. For example, you load data for the current month into the local partition, use the DATACOPY command to copy the entire currency partition that contains the updated data, and then run the conversion on the currency partition.
How can you turn off CCTRACK? You can turn off CCTRACK in three ways: · Use the SET CCTRACKCALC ONOFF command in a calculation script to turn off CCTRACK temporarily · Use the CLEARCCTRACK calculation command to clear the internal exchange rate tables created by CCTRACK.
Set CCTRACK to FALSE in the essbase.cfg file.
What is LRO (Linked reporting objects)? An LRO is an artifact associated with a specific data cell in an Essbase database. LROs can enhance data analysis capabilities by providing additional information on a cell.
An LRO can be any of the following:
· A paragraph of descriptive text (a "cell note")
· A separate file that contains text, audio, video, or graphics
· A URL for a Web site
· A link to data in another Essbase database
How do you create LRO's?
Users create linked objects through Essbase Spreadsheet Add-in for Excel by selecting a data cell and choosing a menu item. There is no limit to the number of objects you can link to a cell. The objects are stored on the Essbase Server where they are available to any user with the appropriate access permissions. Users retrieve and edit the objects through the Essbase Spreadsheet Add-in for Excel Linked Objects Browser feature, enabling them to view objects linked to the selected cell.
Does adding or removing links to a cell does not affect the cell contents?
No.LROs are linked to data cells --not to the data contained in the cells. The link is based on a specific member combination in the database.
Give a few examples of LRO's?
Ex1: A sales manager may attach cell notes to recently updated budget items. Ex2: A finance manager might link a spreadsheet containing supporting data for this quarter's results. Ex3: A product manager might link bitmap images of new products. Ex4: A sales manager may link the URL of a company's Web site to quickly access the info on the Web
How does Essbase locate and retrieve linked objects?
Essbase uses the database index to locate and retrieve linked objects. If you clear all data values from a database, the index is deleted and so are the links to linked objects. If you restructure a database, the index is preserved and so are the links to linked objects.
Do shared members share LRO's?
Shared members share data values but do not share LROs. This is because LROs are linked to specific member combinations and shared members do not have identical member combinations. To link a given object to shared members, link it to each shared member individually.
Can you change the member combination associated with any linked object?
You cannot change the member combination associated with any linked object. To move an object to another member combination, first delete it, then use Essbase Spreadsheet Addin for Excel to re-link the object to the desired member combination.
Why do we need to limit the LRO file sizes for storage conversion?
Because Essbase stores linked files in a repository on the server and, by default, the size is unlimited. Limiting the file size prevents users from taking up too much of the server resources by storing extremely large objects. You can set the maximum linked file size for each application. If a user attempts to link a file that is larger than the limit, an error message displays.
The maximum file size setting applies only to linked files and does not affect cell notes or URLs. The lengths of the cell note, URL string, and LRO descriptions are fixed.
What is partitioning?
A partition is the piece of a database that is shared with another database. An Essbase partitioned application can span multiple servers, processors, or computers.
What is Essbase Partitioning?
Essbase Partitioning is a collection of features that makes it easy to design and administer databases that span Essbase applications or servers. Partitioning is licensed separately from Essbase.
What are the types of Partitions available in Essbase?
Three types of partitions are there.
1. Transparent partition:
A form of shared partition that provides the ability to access and manipulate remote data transparently as though it is part of your local database. The remote data is retrieved from the data source each time you request it. Any updates made to the data are written back to the data source and become immediately accessible to both local data target users and transparent data source users
2. Replicated Partition:
A portion of a database, defined through Partition Manager, used to propagate an update to data mastered at one site to a copy of data stored at another site. Users can access the data as though it were part of their local database.
3. Linked Partition:
A shared partition that enables you to use a data cell to link two databases. When a user clicks a linked cell in a worksheet, Essbase opens a new sheet displaying the dimensions in the linked database. The user can then drill down those dimensions.
What is the process for designing a partitioned database?
Here is the suggested process for designing a partitioned database.
1. Learn about partitions.
2. Determine whether the database can benefit from partitioning.
3. Identify the data to partition.
4. Decide on the type of partition.
5. Understand the security issues related to partitions.
What are the parts of partition?
Partitions contain the following parts,
· Type of partition: A flag indicating whether the partition is replicated, transparent, or linke
· Data source information: The server, application, and database name of the data source.
· Data target information: The server, application, and database name of the
data target.
· Login and password: The login and password information for the data source and the data target.
· Shared areas: A definition of one or more areas, or sub cubes, shared between the data source and the data target.
· Member mapping information: A description of how the members in the data source map to members in the data target.
· State of the partition: Information about whether the partition is up-to-date and when the partition was last updated.
What are benefits of partitioning?
Partitioning applications can provide the following benefits:
· Improved scalability, reliability, availability, and performance of databases
· Reduced database sizes
· More efficient use of resources
· Data synchronization across multiple databases.
· Outline synchronization across multiple databases.
· Ability for user navigation between databases with differing dimensionality.
Can you define different types of partitions between the same two databases?
No
Can a single database serve as the data source or data target for multiple partitions?
Yes
What is overlapping partition?
An overlapping partition occurs when similar data from two or more databases serve as the data source for a single data target in a partition.
Is overlapping partition valid in all the partitions?
An overlapping partition is allowed in linked partitions, but is invalid in replicated and transparent partitions and generates an error message during validation.
When do you use substitution variables in partitions?
Using substitution variables in partition definitions enables you to base the partition definition on different members at different times.
Can we use attribute values to partition a database?
Yes,You can use attribute functions for partitioning on attribute values. But you cannot partition an attribute dimension.
Can we partition an attribute dimension?
No, we cannot partition an attribute dimension.
What is the limitation on version and mode during partition?
Both ends of a transparent, replicated, or linked partition must be on the same release level of Essbase Server. For example, if the source of a linked partition is on a Release 7.1.2 server, the target must also be
on a Release 7.1.2 server.
In addition, for transparent and replicated (but not linked) partitions, the application mode of both ends of the partitions must be the same--either Unicode mode or non-Unicode mode.
What are the major difference between ASO & BSO?
If we have more dimensions (generally more than 10) then we will go for ASO that simply rollup If we have less dimensions then we will go for BSO We cannot write back in ASO we can write back in BSO Most of the dimensions are sparse in ASO Most of the dimensions are dense in BSO
What is "Enterprise Analytics"? ASO in System 9 is called Enterprise Analytics.
Explain in detail about the features of ASO?
· ASO databases are created specifically to deal with the requirements of very large sparse data sets with a high no of dimensions and potentially millions of members. · ASO do not have indexes or data blocks. · ASO do not use calculation scripts. Bcoz calculations are not complex. · ASO uses a new kind of storage mechanism that allows improved calculation times from 10 to100 times faster than BSO. · ASO can store up to 252 dimensional combinations. · The front end tools usually do not care if the database is ASO or BSO. Even Maxl sees minor differences. · We can have attribute dimensions in ASO. · In ASO there is no concept as dense and sparse dimensions. · We do not have two pass logic and built in time balance functionality.( time balance functionality is present from 9.3 version onwards). · Member formulas are not supported in stored hierarchies. · Only non consolidation (~) and addition (+) operators are supported in shared hierarchies. · We cannot create more than 1 database in ASO. · ASO does not utilize procedural calculation scripts. · ASO formulas are written in MDX syntax. · ASO has Accounts dimension but it is completely different from the account dimension of BSO. · ASO is read-only. You cannot write to ASO databases, but there is a workaround using transparent partitions and pointing to an attached BSO database for those duties. · You can load data to level zero members only. · The database must restructure after any members in the standard dimensions are added ,deleted or moved. In fact most actions on an ASO outline will either cause a loss of data or restructure.
How do you differentiate ASO applications?
You can easily differentiate the ASO database in the Administrative Services Console by the red star beside the application name.
How do you create an ASO application? ASO has two types of hierarchies: stored and dynamic. The dimension can contain both types of hierarchies (if you enable multiple hierarchies).Other properties that need to be set for dimensions and members include · Dimension Type · Data Storage(store, never share, label only) · Member solve order
· Alias
You can add dimensions using the visual editor or the rules files.
Unlike in block storage ASO does not allow you to preview the outline changes. If you are unsure of the build file, make a backup of your outline before running the new build rule. For ASO databases after the data values are loaded into the level 0 cells of an outline, the database requires no separate calculation step. For retrieving from the ASO database, retrieve and analyze just as in BSO database.
How do you create an ASO database using ASO Outline Conversion Wizard ? You can also create an ASO database using ASO Outline Conversion Wizard. This wizard uses the existing BSO database to convert to an ASO database. This is advantageous because we do not need to create an ASO database from the Scratch. However we need perform reengineering of dimensions and hierarchies.
How do you create ASO in the Automated Way? The final way of creating an ASO application is by using "Create Application" , "Create Database" ,"Create Outline " commands using MaxL. Typically this method is used when you are running the MaxL command as a part of the batch job.
**Unicode is supported for BSO databases only.
**Data Mining is not supported by ASO databases.
**MDX is the only mechanism for defining member calculations in databases.
Unicode applications use UTF-8 encoding form to interpret and store character text, providing support for multiple character sets.
To set up a Unicode application
1. Setup a computer for Unicode support by doing one of
· Install the for that supports UTF-8 encoding
· Install a Unicode editor
2. Set the Essbase server to Unicode Mode via Administrative Services or MaxL.
3. Check the Unicode box when creating a new Unicode -mode application.
4. You can also migrate from non-Unicode applications to Unicode applications (but not the other way round).
Report Scripts are outdated but still can be helpful when extracting subsets of data from Essbase for online backups or feeding into other systems.
The Wizards Tab of Administrative Services Console menu has the following
components
1. Migration
2. Aggregate Storage Outline Conversion
3. Aggregate Storage Partition
4. User Setup
5. Data Mining Wizard
Thursday, January 14, 2010
Smart View retrieve Error
The error she received is as follows:
"The request timed out. Contact your administrator to increase netRetrycount and netRetryInterval"
Eventhough I increased NetDelay and NetRetrycount in essbase.cfg, but that does not resolve this problem. She was using IE7 on XP SP3.
Here is the reason and resolution for the issue:
By design, Internet Explorer imposes a time-out limit for the server to return data. The time-out limit is five minutes for versions 4.0 and 4.01 and is 60 minutes for versions 5.x and 6. Also, the time-out limit is 30 seconds for Windows Internet Explorer 7. As a result, Internet Explorer does not wait endlessly for the server to come back with data when the server has a problem.
Apparently the query which the user was running takes around 45 seconds. The IE7 time out setting was causing it to error out.
we need to change (add) three new registry keys to resolve the issue.
- Open the Registry (Start -> Run -> Regedit)
Locate the following section:[HKEY_CURRENT_USER\Software\Microsoft\Windows\CurrentVersion\Internet Settings]\ - Create the following new keys for dword with decimal values:
"ReceiveTimeout"=dword:00dbba00
"KeepAliveTimeout"=dword:00180000
"ServerInfoTimeout"=dword:00180000 - Restart the machine for the new settings to take effect
If the above settings does not make any difference and the version of SmartView is 9.3.1.2, it may need to upgrade SmartView 9.3.1.4 or higher version.
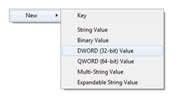
Here are the Screen shots for changing the registry settings.
Right click and select DWORD (32-bit) value
Rename to KeepAliveTimeout
Friday, October 2, 2009
Correct Order of restarting planning services
here is the order you have to follow to restart.
Stop Order
Planning Service
RMI registry
AAS
Start Order
AAS
RMI registry
Planning Service
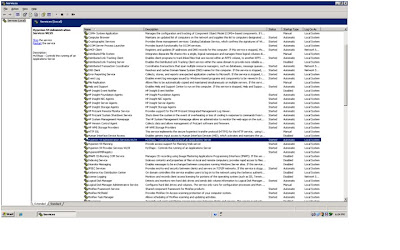
Screen shots of services shown below:
Thursday, September 10, 2009
Hyperion Essbase Overview
What is Essbase OLAP server?
An OLAP server is a multidimensional database for storing data with an unlimited number of dimensions such as time, region, accounts, channel or products. Essbase server manages analytical data models, data storage, calculations, and data security.
What are the Essbase Application tools?
Applications tools are used for extending Essbase applications
Spreadsheet Add-in
Smart view for Microsoft applications
Currency Conversion
Essbase SQL interface
Essbase Application Programming Interface (API)
What is Partitioning?
Copying a slice of a large database to work with it locally, or link from your database directly to other databases.
What is a Hybrid Analysis?
Hybrid analysis integrates relational databases with Essbase databases to combine the size and scalability of the relational database with conceptual power and analytical capabilities of the multidimensional Database.
What are administrative requests and client requests?
Administrative requests such as
· Logging in and logging out
· Starting and stopping applications and databases,
· Viewing users security information
are handled by the Essbase server agent
Client requests such as
Data loads
Spread sheet reports
Data lock and unlock
are handled by the application server (ESSVR)
What is the use of multidimensional database such as Essbase?
Multidimensional database supports multiple views of data sets for users who need to analyze the relationships between data categories.
For example marketing analyst needs detailed information in different view than the manager.
Multidimensional DB consolidates and calculates data to provide different views. Only Database outline, the structure that defines all elements of the DB, limits the number of views
With the multidimensional DB users can pivot the data to see information from different view point, drill down to find more detailed information or drill up to see an over view.
Relational database have more data and have all transactions information. Whereas the Essbase has limitations on data which it can hold. In Essbase the filters (security) can be given until the data cell value. Whereas in RDBMS the security can be given only until table view. In RDBMS we can see only one view.
What are Standard dimensions?
Standard dimensions are those which represent the core components of the business plan an often relate to the departmental functions
Examples of standard dimensions are as follows
Time
Accounts
Products
Market
Dimension
Dimensions are static in most databases. DB dimensions rarely change over the life of an application.
What is an Outline?
Outline is the structure that defines all elements of the Database. It dictates how data is to be stored into the database. Outline defines the structural relationship between the members in DB. Organizes all data in the DB
Defines consolidations and mathematical relationships between members
It defines type of dimensions. Aliases, member formulas etc.
The order of the outline is that how dimensions are arranged is as follows:
Dense dimensions followed by sparse dimensions followed by Attribute dimensions.
How do you order the Outline?
All the attribute dimensions should be placed at the end of the outline. Dense dimensions should be placed in the first then followed by the sparse dimensions
The order determines
How quickly calculations are run
How long it takes users to retrieve information
The order of the outline for query performance
· Dense
· Most queried Sparse
· Least queried Sparse
· Most queried Attribute
· Least queried Attribute
The order of Outline for Calculation time
· Dense
· Smallest Sparse dimension
· Largest Sparse
· Smallest Attribute
· Largest Attribute
What is the highest level of consolidation in the outline?
Dimension
Is there any limitation on number of members?
No. Essbase does not limit the number of members within a dimension and allows you to add new members as needed.
Parent is a member, which has a branch below it.
Child is a member, which has a parent above it.
Siblings are the child members of same immediate parent, at the same generation.
Descendants are all members in branches below a parent.
Ancestors are all members in above a member.
Root is a top member in a branch.
Leaf member has no children.
Generation number refers to the consolidation levels within a dimension.
Level also refers to a branch within a dimension.
What is a cell/data value?
A data value is defined by the intersection of all standard dimensions in the database.
What is the maximum number of values in the database?
Product of members in each dimension
Why do we need to have classification as dense and sparse dimensions?
As the data is no smoothly and uniformly distributed and data does not exist for the majority of members. Essbase speeds up data retrieval while minimizing the memory and disk requirements.
A sparse dimension is a dimension with a low percentage of available data positions filled.
A dense dimension is a dimension with a high probability that one or more data points are occupied in every combination of dimensions.
What are the two types of internal structures in Essbase?
Data blocks
Index system
The two types of internal structures are to store data and access data.
What is a Data block?
Data block is a cube created for each unique combination of sparse standard dimension members (provided that atleast one data value exists for sparse member combination).
The Data block represents all the dense dimension members for its combination of sparse standard dimensions.
Its size depends on number of dense dimensions.
How does Essbase calculate the data?
Top down order
What is an Index entry?
The index entry provides a pointer to the data block
Essbase creates Index entry for each data block. The index entry represents the combinations of sparse standard dimensions. It contains an entry for each unique combination of sparse standard dimension members for which atleast one data value exists.
What happens if you make all dimensions sparse?
Data blocks are created for each unique combination of sparse standard dimension members. Thus a large number of dense blocks are created, and thus a huge index containing pointers (or addresses) for all those data blocks.
Huge index consumes large amount of memory. The more index entries the longer Essbase searches to find a specific block.
What happens if you make all dimensions dense?
Only one huge sparse block is created with only one index entry. This block is very sparse. This configuration requires thousands of times more storage than other configurations. Essbase need to load the entire data block into memory when it searches for a data value, which requires enormous amounts of memory.
What is the Design Process?
Analyze business needs and plan the database
Define the database outline
Check the system requirements
Load the test data into the database
Define calculations
Define reports
Verify with the users
Repeat the process
What are the different types of data sources?
Flat files (column formatted)
Spreadsheet files
Any RDBMS files
What is a shared member?
The shared member concept lets two members with the same name share data. The shared member stores only pointer to the data contained in the other member, so the Essbase only stores the data once. Shared members should be in the same dimension.
What dimension can be given time balance properties?
Only accounts dimensions can be given time balance, expense reporting, and country and currency properties.
What is the use of variance reporting?
Variance reporting properties defines how Essbase calculates the difference between actual and budget data in members with @VAR, @VARPER functions in their member formula.
· Expense reporting (Budget-Actual)
· Non-Expense reporting (Actual-Budget)
What is a Function?
It is a predefined routine to carry on specific task or calculation.
What is a formula?
Formulas are used to calculate relationships between members in the DB Outline.
What is a dynamic Calc?
When you tag a member as dynamic calc, Essbase calculates the combinations of the member only when user retrieves data, instead of pre calculating member combinations during the regular DB.
Dynamic calc shorten the regular calc time, but may increase the retrieval time for dynamically calculated data values.
What are the advantages of Dynamic calc?
Low disk space
Reduced database restructure time
Reduced back up time
Optimum regular calculation time
What are the members for which Two-pass calculations can be given?
Accounts
Dynamic calc
Dynamic calc and store
How does a user can view data?
Spread sheet
Printed reports
Reports published on web
web analysis
smart view
Can you load data or calculate data on client machine?
No.
Applications and Databases created on client machine are used only to store database objects, such as outlines and calc scripts. You cannot load or calculate data on a client machine.
What are Database Objects?
Files that are related to databases are called Objects. Common types of objects are:
Database Outlines (.OTL)
Report Scripts (.REP)
Calculation Scripts (.CSC)
Data Load rules and Dimension build rules (.RUL)
Data sources
Security definitions
LRO’s (Linked Reporting Objects)
Partition definitions
What is a rule file?
Data load rules are set of operations that Essbase performs on the data from external data source file as it is loaded, or copied into the Essbase database.
Specifying the data load rules is the most common way to load data into the Database.
Dimension build rule files create or modify an outline dynamically based on the data in the external source file.
What is a calculation script?
Calc script is a text file with set of instructions telling Essbase how to calculate data in the database. It has “. csc” extension.
What is a Report script?
Report script is a text file with a set of instructions on data retrieval, formatting and output to create a report from the database.
Report script has .REP extension.
What is a Linked Reporting Object (LRO)?
A LRO is an object associated with a specific data cell in the Essbase database. A LRO can any of the following:
A paragraph of descriptive text (” cell note”).
A separate file that contain text, audio, video or graphics.
An URL (Uniform Resource Locator).
A link to data in another Essbase database.
What are “.EQD” files?
Within spreads sheet add-in, users can create queries using query designer (EQD). Users can save the reports in the form of queries (.EQD files)
What are “.sel” files?
With the spreadsheet add-in, users can define member retrievals with the member select feature. If users want to save member select specification, they can do so with a “.sel” file.
How can you create a database?
Application manager file>new>database
Essbase administrative services console
ESSCMD (“CREATE DB”)
Maxl (“create database”)
Application and database names should be less than 8 characters.
create application------maxl
CREATEAPP------------ESSCMD
What is annotating database?
It is a database note that can provide useful information in the situations where you need to broadcast messages to users about status of the database deadlines for updates and so on
Select database>set note
What are substitution variables?
Substitution variables act as global placeholders for the information that changes regularly.
Each variable has a value assigned to it. The value can be changed at any time by the DB designer, thus manual changes are reduced. Ex :- currmnth.
You cannot use the substitution variables in formulae that are applied to the DB outline. The value of the substitution variable cannot be more than 256 characters.
Substitution variables can be used only in
Calculation scripts
Report scripts
Spread sheet add-in
SQL interface
Server>substitution variable
Maxl (for creating/deleting/updating)
Alter system
Alter application
Alter db
ESSCMD
CREATE VARIABLE
DELETE VARIABLE
UPDATE VARIABLE
What is a location alias?
A location alias maps an alias name for a DB to the location of that DB.
You can use location aliases only with the @XREF function.
With @XREF function you can retrieve data value from another database to include in calculation in the current database. In this case, the location alias points to the database from which the value to be retrieved.
Database>location aliases
Create
Maxl ----------------------create location alias
ESSCMD----------------CREATE LOCATION
Edit /Delete
Maxl display location alias
drop location alias
ESSCMD LIST LOCATIONS
DELETE LOCATION
What happens if you open outlines in two instances?
If you open same outline with two instances of application manager using same login id, each save will overwrite the changes of the other instance.
Copying database
Database > copy
Maxl create database as
ESSCMD COPYDB
What are important points while building an outline?
· All members and alias names should be unique;
· Only one dimension should be tagged as accounts, time, currency type and country;
· Level “0” members cannot be label only;
· Level “0” members cannot be assigned formulae but dynamic calc members of standard dimensions may have formula;
· Dynamic calc should not have more than 100 children;
· Boolean attribute dimensions have only two members.
What are the restructuring options in saving database?
· All data
· Level 0 data (when all data in the outline is at level 0)
· Input data (when you load data into non level 0 members)
· Discard all data (when you expect to reload data or when outline is radically changed that no existing data applies)
How do you set dense and sparse settings?
Settings>data storage
Data dictionary button
· You must set the standard dimensions with which you plan to associate attribute dimension as sparse because attributes can only be associated to sparse standard dimensions.
· Application manager automatically sets attribute dimensions as sparse.
How do you rename members?
· Data dictionary button
· Edit>properties
· Manually
When does a DB restructure?
When you add, delete, or move non-attribute (standard) dimensions or members, Essbase restructure DB and you must recalculate your data.
What is Metadata?
Metadata is data is data about data. Metadata is the data contained in the database outline that describes the values within a DB.
Ex:
East>New York>cola>sales>10000
East>New York>cola>sales> is metadata
What are different types of dimension tags?
· Time
· Accounts
· Country
· Currency
· Attribute
Can you add time members that are not tagged as time?
Yes
When do you give an accounts tag to a dimension?
You can tag a dimension as accounts if it contains items that you want to measure such as profit or inventory.
Time dimension tag says how often you collect and update data. The time dimension enables several accounts dimension functions such as first and last time balances.
What is the significance of time balance properties?
When you set a time balance property on a member in an accounts dimension, it affects how Essbase calculates the parent of that member in the time dimension.
· TB FIRST (The parent value is the value of the first member in the branch)
· TB LAST (The parent value is the value of the last member in the branch)
· TB AVG (The parent value represents the average value of the children)
· TB NONE (default; rolls up parents in the time dimension in the usual way)
Skip Properties
· None
· Missing
· Zeros
· Missing and zeros
Skip properties, expense reporting, Time Balance properties are applicable only to the accounts dimension.
What is a Two-Pass calculation?
By default Essbase calculates outlines from the bottom up first calculating the values for children and then values for parent. Sometimes however the values of children depend may be based on the values of parent or the values of other members in the outline. To obtain correct values for these members, Essbase must first calculate the outline and then recalculate the members that are dependent on the calculated values of the other members. The members that are calculated on the second pass through the outline are called Two-Pass Calculation.
Only accounts, dynamic calc, dynamic calc and store members can be given two pass calculation.
Edit>properties
Data dictionary button
What does the consolidation properties do?
Member consolidation determines how children roll up into their parents. Default (+) operator.
Essbase don’t use consolidation properties for attribute dimensions.
Essbase automatically tags members of the attribute dimensions as dynamic calc. you cannot change this setting.
When do you use label only?
When no data is associated with members we use label only. They are used only to ease navigation and reporting from the spread sheet add-in.
You cannot associate attributes to label only. If you tag label only to the base member, which has, attributes associated with it, Essbase removes attributes and displays a warning message
Monday, September 7, 2009
Fragmentation in Essbase (BSO)
- What is Fragmentation?
Fragmentation is unused disk space.
- When does Fragmentation occur?
Fragmentation is likely to occur with the following:
Read/write databases that users are constantly updating with data
Databases that execute calculations around the clock
Databases that frequently update and recalculate dense members
Data loads that are poorly designed
Databases that contain a significant number of Dynamic Calc and Store members
Databases that use an isolation level of uncommitted access with commit block set to zero
- How can you measure fragmentation?
You can measure fragmentation using the average clustering ratio or average fragmentation Quotient.
Using the average fragmentation quotient
Any quotient above the high end of the range indicates that reducing fragmentation may help
performance, with the following qualifications:
The reported value of the Fragmentation Quotient is more accurate when there are no other write
transactions running on the database.
For databases less than 50 MB using the Direct I/O access mode, the fragmentation quotient tends to be high. A high fragmentation quotient does not necessarily indicate a need to reduce fragmentation, because the free space is created in 8 MB chunks and all of it might not get used right away.
Database Size | Fragmentation Quotient Threshold |
Small (up to 200 MB) | 60% or higher |
Medium (up to 2 GB) | 40% or higher |
Large (greater than 2 GB) | 30% or higher |
Using the average clustering ratio:
The average clustering ratio database statistic indicates the fragmentation level of the data (.pag) files. The maximum value, 1, indicates no fragmentation.
- How do you can prevent and remove fragmentation?
You can prevent and remove fragmentation:
To prevent fragmentation, optimize data loads by sorting load records based upon sparse dimension members. For a comprehensive discussion of optimizing data load by grouping sparse members.
To remove fragmentation, perform an export of the database, delete all data in the database with CLEARDATA, and reload the export file.
To remove fragmentation, force a dense restructure of the database.













